Residing between 1000 BCE and 300 CE, the Nok culture was one of the very first and most advanced ancient civilizations in Africa, located in modern-day Nigeria. This civilization is especially famous for terracotta sculptures, its peculiar artistic achievements, and the impetus it gave to early West African metallurgy. Even though the Nok people mysteriously disappeared centuries ago, their legacy remains vital in the cultural, artistic, and historical understanding of modern-day Nigeria and West Africa.

The Emergence of the Nok Civilization
The Nok developed their civilization in central Nigeria, mostly in the area around the Jos Plateau, extending into parts of modern Kaduna and Niger states. Discovered in the 1940s by British archaeologist Bernard Fagg, the Nok’s existence was uncovered through a series of accidental finds by tin miners. What they uncovered were elaborately crafted terracotta figures that astounded scholars as some of the earliest known evidence of sophisticated sculpture in sub-Saharan Africa.
The Nok is primarily known for its extremely stylized terracotta statues that range in size from small, naturalistic human heads to complete figures. Many of these sculptures depict hairstyles in detail, jewelry, and other ornamentation; thus, giving a glimpse of the Nok’s social and cultural life. In most Nok artifacts found so far, the findings have been a rather artistic look into the civilization’s engagement with technology and agriculture. The Nok were among the first into such important technological innovations as iron smelting, helping to advance their society and influence other civilizations throughout West Africa.
Art, Culture, and Influence
On the one hand, the Nok sculptures are arguably one of the most tantalizing finds of ancient Africa from a historical point of view. The complexity of the works suggests a very organized, hierarchical society with skilled artisans, doubtless produced for some ritual or ceremonial purpose. At the same time, it was art that made it possible to get some insight – even though incomplete – into the worldview of that civilization, since many of the sculptures depict representations of animals, humans, and mythological figures.
The Nok culture is believed to have influenced other cultures within the same region that came much later, such as Yoruba and Igbo. According to some scholars, it may be possible through these cultures, especially in the form of bronze casting which later became the signatures of the renowned Ife and Benin kingdoms, to trace elements of Nok’s art and religion, as well as the social structure.
The Mysterious Decline
Despite these achievements, for unknown reasons, the Nok civilization began to decline sometime around 300 CE. A variety of other theories exist including environmental change and shifting trade patterns to internal conflict. Unlike their West African neighbors, the Mali or Songhai Empires, there are no written records of the Nok civilization, so most of the information derived from this civilization has to come from archaeological digs.
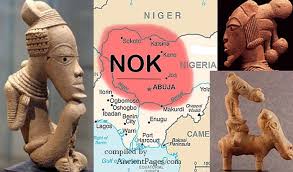
Where are they, and who are they now?
Hence, the Nok civilization was lost well over 1,500 years ago, and none of their direct descendants today could be identified absolutely with the ancient culture of this people. Nevertheless, their legacy lives through the people and the cultural expressions in today’s Nigeria. “The Nok artistic and technological attainments have been incorporated into the broader narrative of Nigerian history, while its influence on later cultures remains a subject of academic debate.” Interest in the Nok civilization has been revived over recent years, with increased efforts toward better preservation and study of the artifacts. Museums in Nigeria and around the world display Nok terracotta sculptures as part of exhibitions extolling the ancient history of Africa. These are not only symbols of the rich heritage of Nigeria but also signs of a contribution that reaches further: the contribution of Africa to early global civilization.
With such advanced artistry, ironworks, and societal structure, the Nok civilization holds a place among the most important early cultures of Africa. Long since gone into history, their presence still lingers in contemporary Nigerian culture and identity. As archaeological research proceeds, further details of the Nok Civilization might appear that can continue to enrich insight into the deep historical roots and legacies of one of the oldest African cultures.

